Data Integration and Migration Design ensures seamless geospatial data integration across platforms, using ETL processes for accuracy and consistency. Land Base Management Design systematically manages geographic data for infrastructure planning, supporting informed decision-making through dynamic updates and spatial analysis techniques.
Data Integration and Migration Design
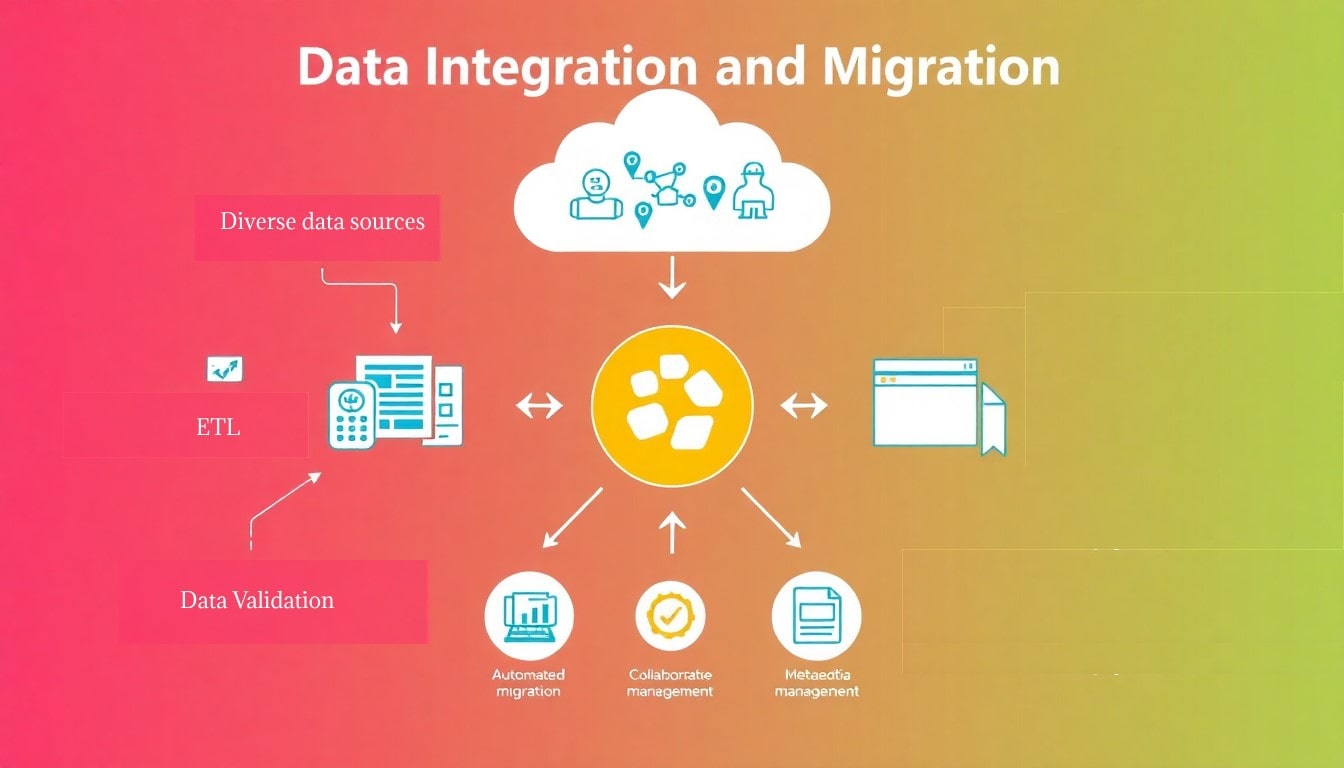
Data Integration and Migration Design focuses on the seamless integration and migration of geospatial data across diverse platforms and formats, ensuring data consistency, accuracy, and accessibility. This process begins with a comprehensive assessment of existing data sources, formats, and systems to identify potential integration challenges and opportunities. The design team employs advanced ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) methodologies to facilitate the extraction of data from multiple sources, followed by transformation processes that standardize and clean the data to ensure compatibility with target systems.
The migration phase involves careful planning and execution, utilizing automated tools and scripts to transfer data with minimal disruption to ongoing operations. This includes the establishment of rigorous data validation and verification protocols to ensure that the migrated data retains its integrity and fidelity. Additionally, the design framework incorporates comprehensive documentation and metadata management, providing users with clear insights into data lineage and transformations.
By ensuring a robust integration strategy, the Data Integration and Migration Design enhances interoperability between systems, allowing for efficient data sharing and collaboration among stakeholders. This capability is critical for supporting decision-making processes in infrastructure projects and ensuring that geospatial data is readily available for analysis and application across various domains.
Process:
- Starts with a comprehensive assessment of data sources, formats, and systems to identify integration challenges and opportunities.
- Utilizes advanced ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) methods to extract, standardize, and clean data for compatibility with target systems.
Migration Phase:
- Carefully planned and executed using automated tools and scripts to minimize operational disruptions.
- Includes rigorous data validation and verification protocols to maintain data integrity and fidelity.
Documentation and Metadata Management:
- Incorporates detailed documentation and metadata for clear insights into data lineage and transformations.
Benefits:
- Enhances interoperability between systems, enabling efficient data sharing and collaboration.
- Supports decision-making in infrastructure projects and ensures geospatial data is accessible for analysis across various domains.
Land Base Management Design
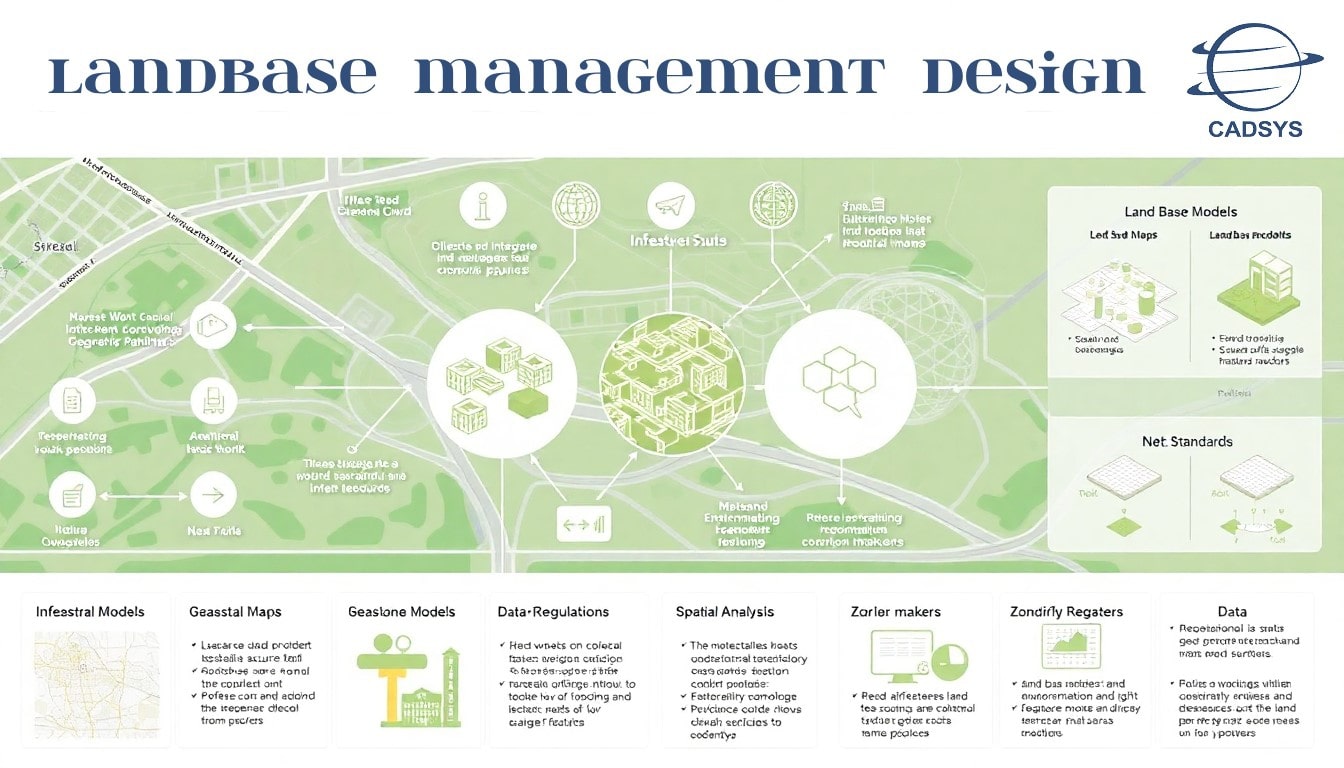
Land Base Management Design entails the systematic management of data related to streets, parcels, and other geographic features, playing a crucial role in infrastructure planning and development. This process begins with the collection and integration of diverse geospatial data sources, including cadastral maps, property records, and municipal planning documents. The design team utilizes advanced GIS tools and methodologies to create comprehensive land base models that accurately represent geographic features and land use patterns.
Key components of the Land Base Management Design include the establishment of data standards and protocols to ensure uniformity and accuracy across the land base database. The design also incorporates spatial analysis techniques to evaluate land use compatibility, zoning regulations, and environmental considerations, which are essential for informed planning and development decisions.
Furthermore, the design framework supports dynamic updates and maintenance of land base data, enabling stakeholders to access current information regarding property boundaries, ownership, and land use changes. By providing a reliable and detailed representation of geographic features, the Land Base Management Design facilitates effective collaboration among planners, engineers, and decision-makers, ultimately leading to optimized infrastructure development and resource allocation.
Process:
- Begins with collecting and integrating geospatial data, including cadastral maps, property records, and municipal planning documents.
- Uses advanced GIS tools to develop comprehensive land base models representing geographic features and land use patterns.
Key Components:
- Establishes data standards and protocols for uniformity and accuracy in the land base database.
- Incorporates spatial analysis to evaluate land use compatibility, zoning, and environmental factors for informed planning.
Dynamic Updates:
- Supports real-time data maintenance, providing stakeholders with up-to-date information on property boundaries, ownership, and land use changes.
Benefits:
- Enables effective collaboration among planners, engineers, and decision-makers.
- Optimizes infrastructure development and resource allocation through accurate geographic data.